Cleanroom Air Shower Technology and Efficiency
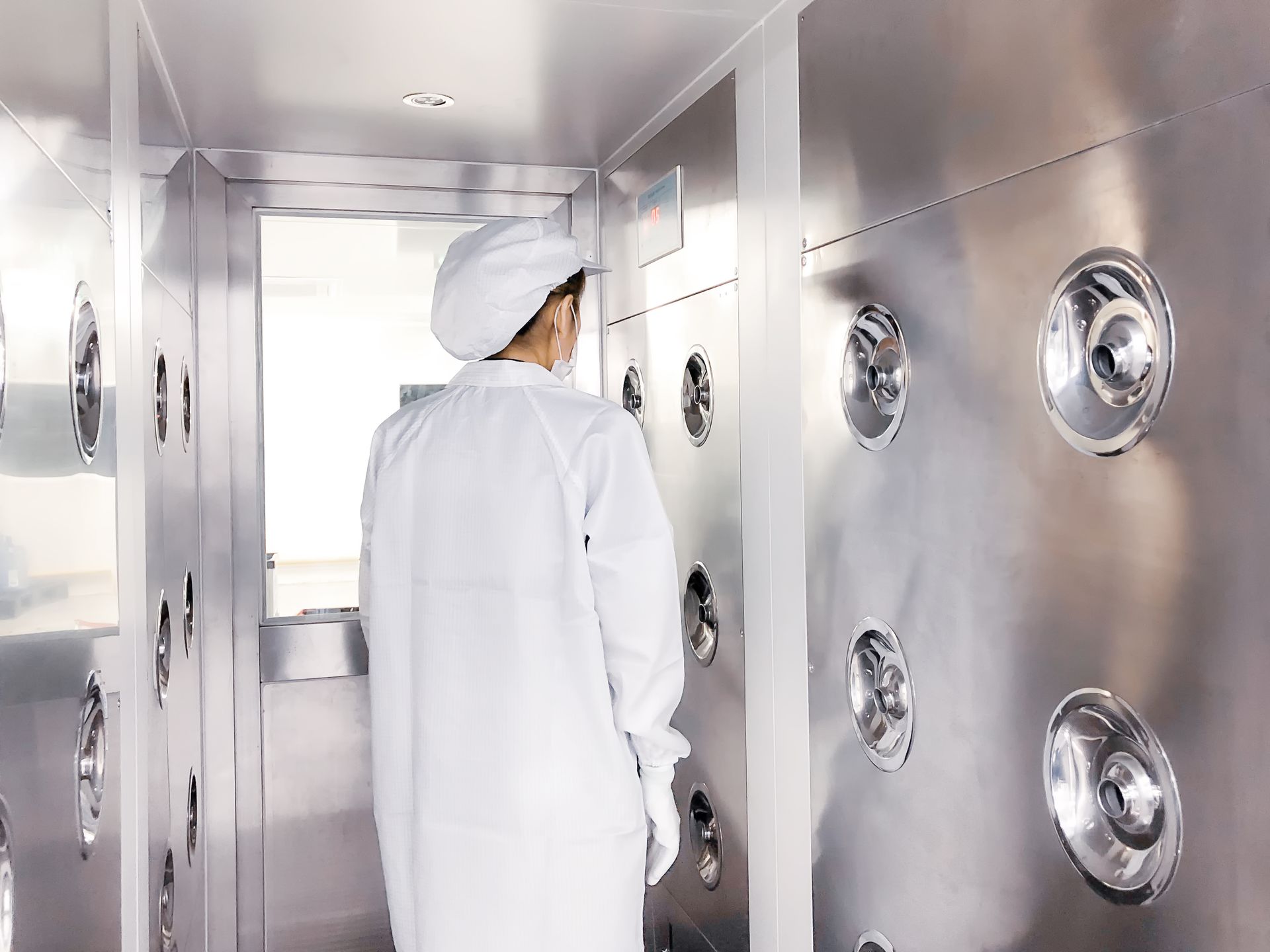

Cleanroom Air Shower Technology and Efficiency
Cleanrooms are meticulously designed environments where contamination control is of paramount importance. They are widely used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace, and medical device production, where even the smallest contaminants can compromise product quality and safety. In these controlled environments, maintaining high standards of cleanliness requires a multi-faceted approach, including the use of specialized equipment such as air showers.
An air shower is a crucial part of cleanroom infrastructure designed to reduce the risk of contamination by removing particles, dust, and other potential contaminants from personnel and materials before they enter the cleanroom. This technology has become an integral part of contamination control systems in cleanroom operations. In this article, we will explore how cleanroom air shower technology works, its role in enhancing efficiency, and how it contributes to maintaining stringent contamination control standards.
What is a Cleanroom Air Shower?
A cleanroom air shower is a specially designed chamber used to decontaminate individuals, tools, or equipment before they enter a cleanroom. It operates by using high-velocity air jets to blow particles, dust, and other contaminants off of the clothing and surfaces of the person or materials entering the cleanroom. The air is typically filtered through high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters or ultra-low penetration air (ULPA) filters, ensuring that the air used in the shower is clean and free from particles.
Air showers are typically located at the cleanroom’s entrance, serving as a transition zone between the surrounding, non-controlled environment and the cleanroom itself. In many cases, air showers are also used to cleanse materials and equipment that need to be sterilized or decontaminated before entering the cleanroom.
How Does an Air Shower Work?
An air shower uses a system of high-pressure air jets to create a blast of air that dislodges particles and contaminants from the surfaces of objects or individuals. Here's a detailed breakdown of the air shower process:
- Entry into the Air Shower: The individual or equipment enters the air shower chamber, typically through a self-closing door or automatic sliding door. The door automatically locks to prevent any contamination from entering the cleanroom.
- Activation of the Air Jets: Once inside, sensors detect the person’s presence and activate the air shower system. High-velocity air jets positioned on the walls, ceiling, and floor of the chamber direct airflow at the person or object from all angles. These jets create turbulent airflows, which effectively dislodge and blow away particles, dust, and debris from the surface of the person’s gown, hair, or materials.
- Filtration of Air: The air used in the shower is filtered through HEPA or ULPA filters, which are capable of trapping particles as small as 0.1 microns (HEPA) or 0.03 microns (ULPA). This ensures that the air inside the air shower remains free from contaminants that could undermine the cleanliness of the cleanroom environment.
- Exhaust and Recirculation: After passing over the person or object, the contaminated air is either vented outside the facility or recirculated through the filtration system. Some systems may use a combination of both exhaust and recirculation to reduce energy costs and maintain air pressure consistency in the cleanroom.
- Exit from the Air Shower: After the designated shower cycle (usually ranging from 20 to 60 seconds), the air shower system deactivates, and the individual or material can exit the chamber through another door into the cleanroom, now free of contamination.
Types of Air Showers
There are several types of air showers designed to cater to different cleanroom needs and configurations. The main distinctions in air shower design include:
1. Personal Air Showers
These are the most common type of air showers, designed for individuals who must enter a cleanroom. They are typically equipped with air jets positioned to direct airflow over the body, face, and shoes, ensuring that contaminants are effectively removed from personnel before entering the cleanroom.
2. Material and Equipment Air Showers
Material air showers are designed to clean materials, tools, or equipment before they enter the cleanroom. These showers may have additional features such as adjustable airflow settings or larger chambers to accommodate bulkier items. Equipment air showers are critical for industries like semiconductor manufacturing, where equipment contamination can lead to costly defects in production.
3. Pass-Through Air Showers
These air showers are designed for both personnel and materials, allowing for both to pass through the chamber. Typically, these air showers have doors on both sides and provide a decontamination process for items before they are brought into the cleanroom, ensuring that both humans and equipment are cleaned before entering the sterile environment.
4. Multi-Station Air Showers
These systems are designed to accommodate multiple people at once and are typically found in larger cleanroom operations. They offer a higher throughput for personnel and can be equipped with more air jets to ensure thorough cleaning.
Efficiency and Benefits of Air Showers in Cleanroom Operations
Air showers offer significant advantages in maintaining cleanroom efficiency and enhancing contamination control. These benefits include:
1. Particle Removal and Contamination Control
The primary role of an air shower is to remove airborne particles from the surfaces of people, tools, and materials. The powerful air jets dislodge dust, skin cells, and other particulates from individuals and equipment, preventing contamination before it can affect the cleanroom. This minimizes the risk of contamination of critical areas or sensitive products in the cleanroom environment.
By effectively reducing the number of contaminants entering the cleanroom, air showers contribute to maintaining the ISO cleanliness classification standards, ensuring that the cleanroom environment meets regulatory compliance.
2. Efficiency in Contamination Control
The air shower is an efficient method of decontamination because it operates quickly and requires minimal manual intervention. Typically, an air shower cycle lasts only about 20-60 seconds, making it a fast and effective solution for contamination control. This short cycle time allows for a high throughput of personnel and materials without significantly interrupting the workflow or delaying production processes.
3. Reduced Risk of Cross-Contamination
Air showers help reduce cross-contamination between the cleanroom and non-controlled environments. Without air showers, particles from everyday clothing, shoes, and equipment could be carried into the cleanroom, compromising the environment. By introducing a step that decontaminates individuals and materials, air showers serve as a barrier that helps isolate the cleanroom from external contaminants.
4. Energy Efficiency
Modern air shower systems are designed to be energy-efficient while still maintaining the necessary level of contamination control. Many air shower systems are equipped with variable airflow controls, which adjust the intensity of the air jets based on the cleanliness of the incoming person or material. Additionally, recirculating air systems can further reduce energy consumption by reusing filtered air instead of continuously exhausting it.
5. Enhanced Worker Safety
Air showers also enhance worker safety by ensuring that cleanroom personnel are not inadvertently carrying contaminants into the cleanroom. By providing a reliable and efficient way to remove particles, air showers help ensure the safety of workers in industries that require sterile environments, such as pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
Air showers are a cost-effective solution for contamination control, particularly when compared to the high costs associated with handling contamination-related product defects or regulatory non-compliance. In cleanrooms where contamination risks can lead to significant financial losses (e.g., pharmaceutical recalls or semiconductor product defects), investing in effective air shower technology can prevent costly mistakes and increase operational efficiency.
Challenges and Considerations in Air Shower Design and Usage
Despite the advantages, there are several challenges and considerations when implementing air showers in cleanroom environments:
1. Space Constraints
Air showers require a certain amount of space to function effectively, particularly in larger operations. In smaller cleanroom setups or facilities with limited floor space, it may be challenging to install an air shower without compromising the overall design and workflow.
2. Maintenance and Upkeep
While air showers are designed to be low-maintenance, regular cleaning and servicing are necessary to maintain their efficiency. Air filters must be replaced periodically, and the air jets must be cleaned to prevent clogging or loss of airflow. Additionally, air showers need to be monitored regularly to ensure they are functioning as intended, without malfunctions that could lead to contamination risks.
3. Personnel Compliance
To maximize the effectiveness of an air shower, personnel must follow proper procedures, including removing personal items like jewelry or bags that could introduce contaminants. Ensuring that employees adhere to these protocols can be a challenge, particularly in high-pressure environments where speed and efficiency are essential.
4. Noise Levels
High-velocity air jets can produce significant noise levels, which may be disruptive to workers. Noise-reducing designs, such as sound-dampening materials and improved airflow mechanisms, can help minimize this issue but should be considered when selecting or designing air showers.
Conclusion
Cleanroom air shower technology plays a critical role in maintaining the integrity and cleanliness of controlled environments. By using high-velocity air jets to remove particulate contamination, air showers provide an efficient, fast, and cost-effective method for decontaminating personnel and materials before they enter the cleanroom. The integration of air showers into cleanroom design ensures that contamination risks are minimized, regulatory compliance is met, and operational efficiency is enhanced.
While air shower technology offers many benefits, it is important to carefully consider the challenges of space, maintenance, and personnel compliance to ensure its effectiveness. In industries where contamination control is vital, air showers are an indispensable tool for protecting product quality, maintaining sterile environments, and ensuring the safety of the manufacturing process. As technology evolves, air shower systems will continue to improve, offering even more efficient and sustainable solutions for cleanroom environments.
Read more: All About Cleanrooms - The ultimate Guide