The Global Impact of Cleanrooms on Manufacturing
The Global Impact of Cleanrooms on Manufacturing
1 Introduction
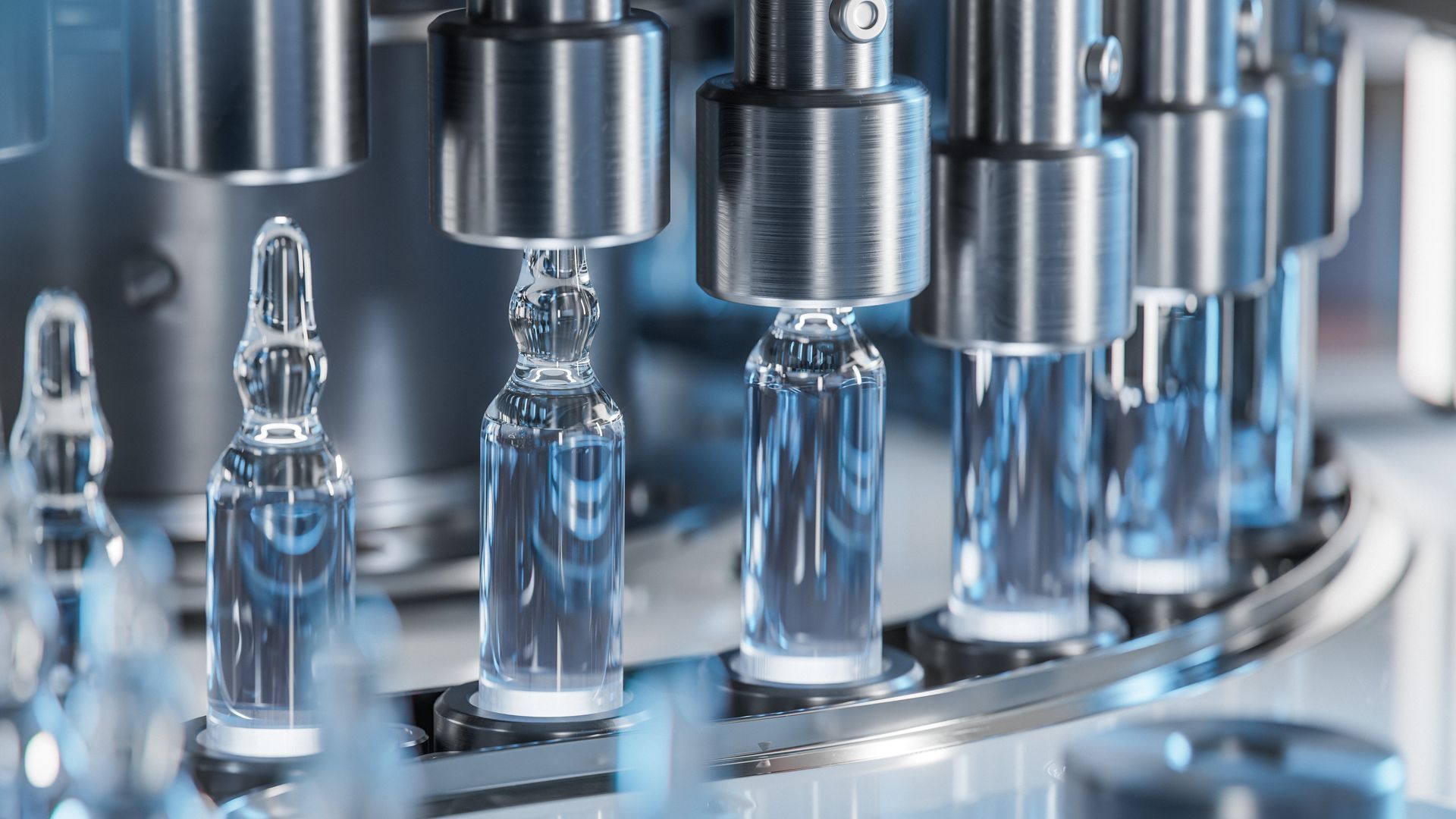
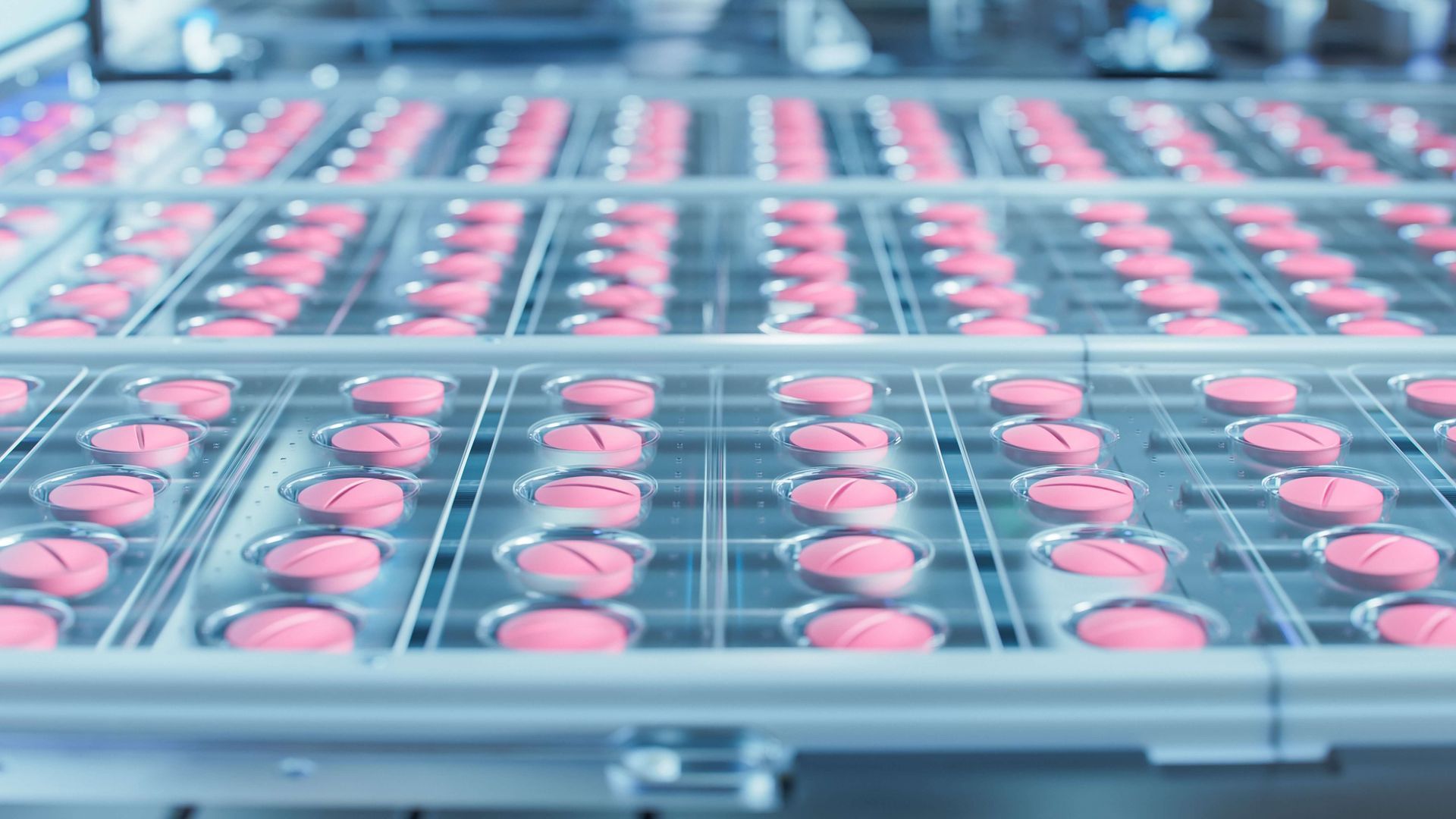
Cleanrooms have become an essential infrastructure component across global manufacturing, enabling industries to achieve unprecedented levels of precision, reliability, and contamination control. As product tolerances shrink and regulatory expectations intensify, cleanrooms allow manufacturers to produce consistent, defect-free outputs at scale. Their influence extends far beyond traditional sectors like pharmaceuticals and semiconductors—cleanrooms now shape advancements in aerospace, biotechnology, optics, medical devices, and emerging nanotechnologies.
This article examines how cleanrooms drive global manufacturing capability, quality, and innovation.
2 Cleanrooms as Enablers of High-Precision Manufacturing
Cleanrooms provide the controlled environment required for products where microscopic contaminants can compromise performance, safety, or functionality. By regulating airborne particles, microorganisms, humidity, temperature, and electrostatic conditions, cleanrooms enable:
- Ultra-fine geometries in semiconductor devices
- High-purity pharmaceutical and biologic production
- Precision assembly of medical implants
- Manufacturing of defect-free optical components
- Reliable fabrication of aerospace and defense technologies
Without controlled environments, many modern products would be impossible to manufacture consistently.
3 Growth of Cleanrooms Driven by Technological Advancement
Global demand for cleanrooms has expanded alongside emerging manufacturing technologies.
Key drivers include:
- Shrinking semiconductor nodes that require ISO 3–5 environments.
- Biopharmaceutical expansion, including cell and gene therapies requiring aseptic or Grade A/B conditions.
- Advanced materials and nanotechnology, which depend on ultra-low particulate levels.
- Battery and energy-storage manufacturing, where contaminants degrade product performance.
- Medical device miniaturization demanding tight contamination control.
As industries evolve toward higher performance and tighter tolerances, cleanroom infrastructure has become increasingly indispensable.
4 Cleanrooms Supporting Global Supply Chain Reliability
Manufacturers rely on cleanrooms to ensure stable, reproducible production across global facilities.
Cleanroom-controlled processes reduce variability and help companies:
- Meet international quality standards
- Harmonize production across regions
- Reduce defect rates and waste
- Maintain supply chain continuity
- Demonstrate compliance during global audits
Standardized cleanroom design and operation also support technology transfer between manufacturing sites, enabling multinational firms to scale rapidly.
5 Regulatory Influence on Cleanroom Manufacturing
Many industries operate under stringent regulatory frameworks that directly dictate cleanroom use.
Examples include:
- GMP for pharmaceuticals and biologics, requiring controlled environments for aseptic fills, sterile filtration, and packaging.
- ISO 14644 standards guiding classification, testing, and monitoring across most cleanroom sectors.
- ISO 13485 requirements for medical device manufacturing environments.
- Aerospace and defense standards requiring rigorous contamination-control planning.
- Industry-specific environmental and safety regulations affecting chemical and nano-material use.
Cleanrooms help manufacturers meet these obligations and maintain globally recognized compliance certifications.
6 Impact on Product Quality and Yield
Cleanrooms directly influence product yield, consistency, and performance.
With controlled environments:
- Defects related to airborne particles are minimized.
- Microbial contamination risks in sterile products are reduced.
- Surface cleanliness remains predictable during assembly.
- Complex devices can be produced with higher reliability.
- Rework, scrap, and batch failures decrease significantly.
This yields major economic benefits—higher throughput, improved efficiency, and greater customer trust.
7 Cleanrooms as Innovation Accelerators
Cleanroom environments make it possible to push technical limits in research and production.
Their global impact includes enabling:
- Development of next-generation semiconductor architectures
- Manufacturing of biologics and personalized medicine
- Precision optical coatings for space and defense
- Advanced robotics and sensor technologies
- Emerging quantum computing hardware
- Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and nanofabrication
Innovation often relies on the ability to control contamination to levels that support new material science and manufacturing precision.
8 Expansion into Emerging Markets
As high-tech industries globalize, cleanroom infrastructure is rapidly expanding into emerging markets.
Countries investing heavily in cleanroom-enabled manufacturing include those developing:
- Semiconductor fabs
- Vaccine and biologics facilities
- Battery and energy-storage plants
- Aerospace supply chains
- Optical and photonics production hubs
This expansion strengthens local economies, diversifies global supply chains, and increases access to advanced manufacturing technologies worldwide.
9 Economic Benefits and Workforce Development
Cleanroom manufacturing generates significant economic value by:
- Creating high-skill technical jobs
- Supporting engineering, construction, and validation industries
- Enabling export-driven manufacturing sectors
- Increasing national competitiveness in high-value markets
- Supporting local supply chains for components, consumables, and equipment
Operating a cleanroom also requires specialized training, driving development of a more technically qualified workforce.
10 Environmental and Energy Considerations
Cleanrooms are energy-intensive due to high airflow rates, filtration stages, and strict environmental controls.
Their global impact includes increasing emphasis on:
- Energy-efficient HVAC systems
- Low-resistance HEPA/ULPA filters
- Variable-speed fan filter units
- Optimized air change rates driven by monitoring data
- Sustainable construction materials
- Life-cycle cost analysis and predictive maintenance
Modern cleanroom design increasingly balances performance with environmental responsibility.
11 Standardization and Global Consistency
ISO 14644 has become the universal reference for environmental classification and testing, enabling consistent cleanroom operation worldwide.
Global standardization supports:
- Predictable quality across international facilities
- Cross-border product approvals
- Supplier and partner alignment
- Harmonized training and qualification programs
- Uniform validation and monitoring requirements
This standardization strengthens manufacturing reliability at the global scale.
12 Cleanrooms and the Future of Manufacturing
Cleanrooms will play a central role in emerging technologies and next-generation production systems.
Future trends likely include:
- Increased use of mini-environments and isolator technologies
- Integration of real-time monitoring and smart building controls
- Expansion of modular and scalable cleanroom systems
- Growth in high-purity material production
- Greater reliance on automation to reduce human contamination
As industries continue to innovate, cleanrooms will remain critical infrastructure for precision manufacturing.
13 Conclusion
Cleanrooms have reshaped global manufacturing by enabling ultra-clean environments that support high-precision, high-reliability production. From semiconductors and biopharmaceuticals to aerospace and nanotechnology, cleanrooms ensure product quality, regulatory compliance, and operational stability across the world. Their impact extends beyond individual facilities—cleanrooms strengthen supply chains, drive economic growth, and enable the technological advancements that define modern industry. As emerging technologies demand even tighter environmental control, cleanrooms will continue to be a cornerstone of global manufacturing excellence.
Read more here: About Cleanrooms: The ultimate Guide